有了二叉树的基础, 我们继续学习二叉搜索树.
二叉搜索树的定义
二叉查找树(Binary Search Tree, 简称”BST”), 又名”二叉搜索树”或”二叉排序树”:
它或者是一棵空树,或者是具有下列性质的二叉树: 若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值; 若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值; 它的左、右子树也分别为二叉排序树。
注 :
我们本文中二叉树的二叉链式存储方案的代码表示为typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{
void *data;
BinaryTreeNode *LeftNode;
BinaryTreeNode *RightNode;
}BTN, *BTNP;
二叉搜索树的查询
BTNP SearchBST(BTNP btnp, char key_data) |
二叉搜索树的插入
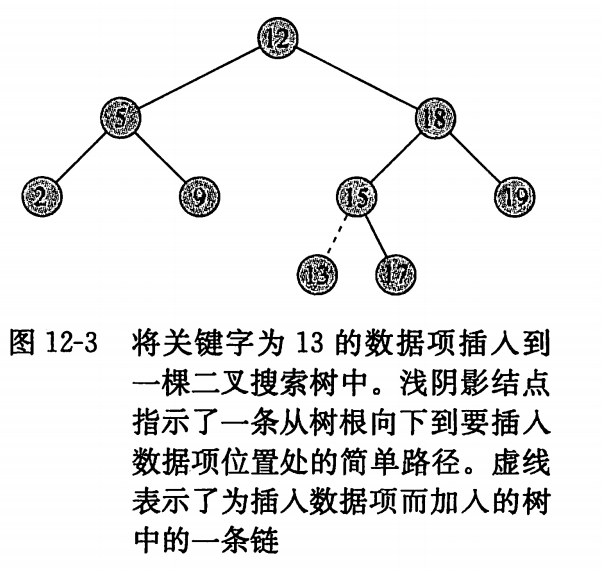
void InsertBST(BTNP &btnp, char key_data) |
二叉搜索树之删除某个结点

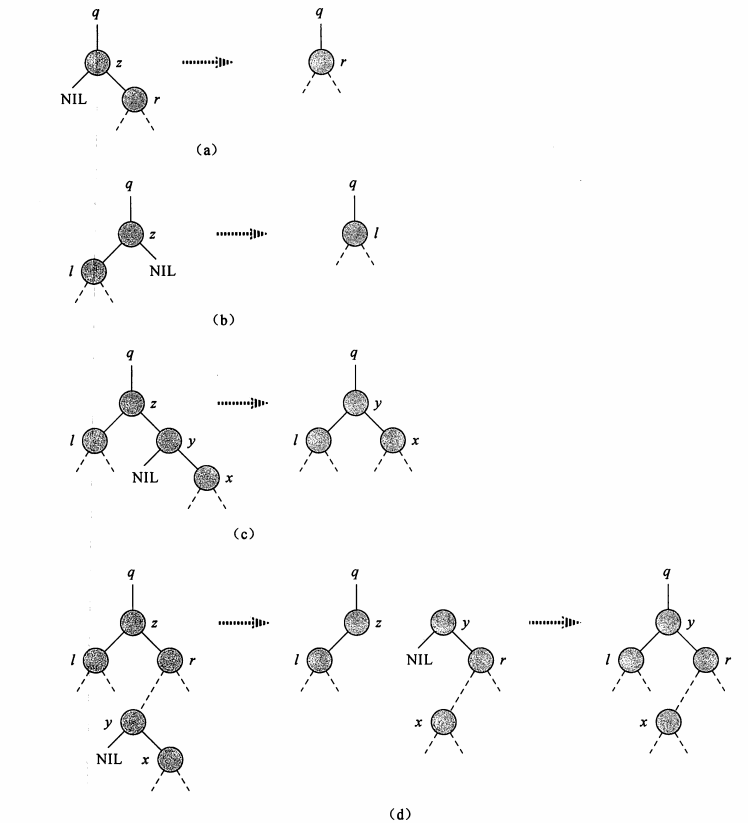
|
二叉搜索树之找最低公共祖先
给定二叉搜索树(BST)中两节点,找出他们的最低公共祖先(LeastCommonAncestors, 简称LCA)。
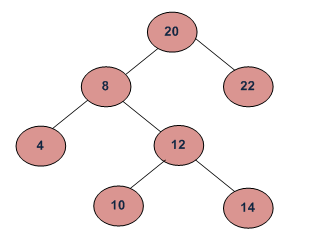
例如对于本文第一张图的LCA为 :
- LCA(4, 14)=8;
- LCA(8, 10)=8.
思路:
利用BST的性质, 假设n1,n2都在BST中,并且n1 < n2。则有 :
- 在遍历过程中,遇到的第一个值介于n1和n2之间的节点n,也即n1 =< n <= n2, 就是n1和n2的LCA。
- 在遍历过程中,如果节点的值比n1和n2都大,那么LCA在节点的左子树。
- 在遍历过程中,如果节点的值比n1和n2都小,那么LCA在节点的右子树。
void LeastCommonAncestorsBinaraySearchTree(BTNP btnp, char key1, char key2) |
参考
<< 算法导论 >>