二叉树的二叉链式存储方案的代码表示:
1 | typedef struct BinTreeNode |
二叉树的遍历
二叉树的广度优先遍历
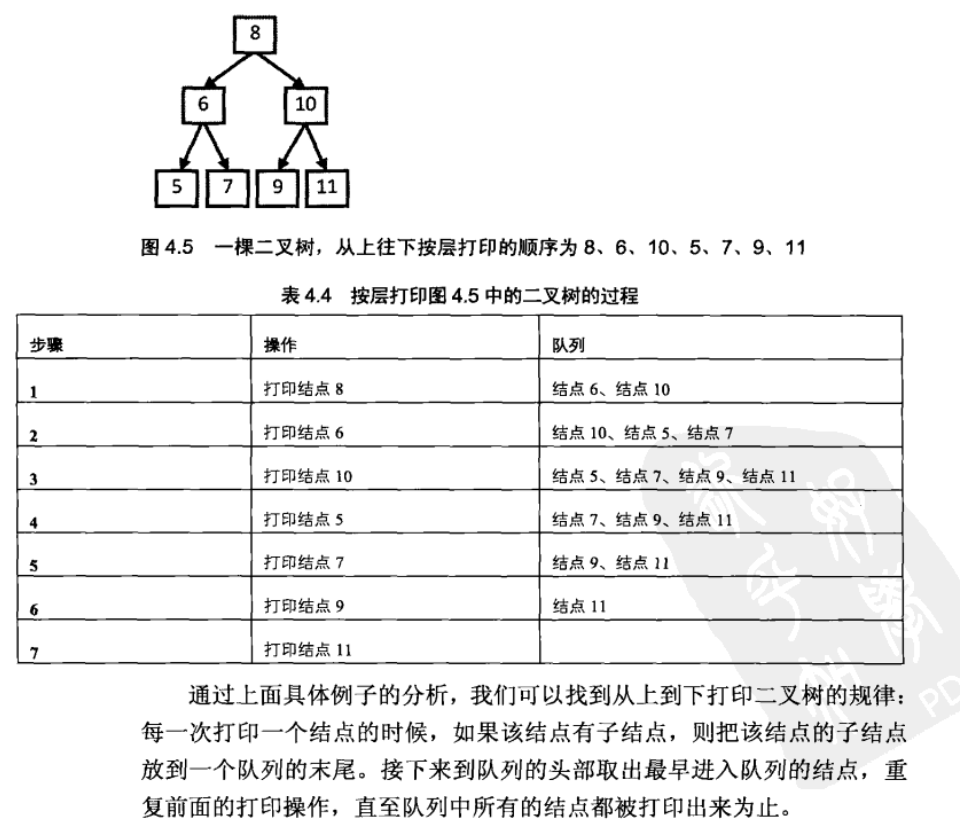
1 | void BreadthFirstTraverse( btnp bTreeNode ) |
深度优先的递归式遍历
递归式遍历的代码实现非常简洁, 但生产环境一般不允许递归, 因为怕栈溢出.
1 |
|
深度优先的迭代式遍历
递归的本质就是出栈入栈, 所以我们用栈来模拟递归, 写出以下三种迭代式遍历
迭代的二叉树三种遍历方式其实思想是统一的 :
都是从左子树的各个结点依次入栈, 当左边已经走到头了, 就开始走右边, 在适当的条件就出栈, 只是每个遍历方式的出栈条件不一样而已, 或者是打印结点的时机不同而已.
迭代式先序遍历代码实现
用栈(Stack)的思路来处理问题。
前序遍历的顺序为根-左-右,具体算法为:
- 把根节点 push 到栈中
- 循环检测栈是否为空,若不空,则取出栈顶元素,保存其值
- 看其右子节点是否存在,若存在则 push 到栈中(因为前序遍历的顺序为根-左-右, 而stack是先进后出的, 所以要先push右子节点)
- 看其左子节点,若存在,则 push 到栈中。
这个cpp版本没有本文下面的go版写得好, 那个更容易理解1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24void PreOrderTraverseNonRecursion( btnp bTreeNode )
{
if ( !bTreeNode )
{
return;
}
std::stack<btnp> tempStack;
while ( !tempStack.empty() || bTreeNode )
{
while ( bTreeNode )
{
cout << bTreeNode->data_ << endl;
tempStack.push( bTreeNode );
bTreeNode = bTreeNode->left_;
}
if ( !tempStack.empty() )
{
bTreeNode = tempStack.top()->right_;
tempStack.pop();
}
}
}
迭代式中序遍历代码实现
1 | void InOrderTraverseNonRecursion( btnp bTreeNode ) |
迭代式后序遍历代码实现
后序遍历的出栈条件有点不一样, 因为后序是先左后右再中的, 比如某个结点p要出栈, 需要遍历完了p的所有右子树之后才能出栈, 而不能第一次就出栈, 所以专门构造了一个结构体PostOrderBT来记录他是否是第一次出栈 (PostOrderBT结构体里有个 isFirstTime_ 的数据来记录)
所以我们代码中的思路就是 :
把每个将要入栈的结点的 isFirstTime_ 标志都置为 true , 当第一次遍历到结点p的时候, 不使p出栈, 但使p的 isFirstTime_ 标志变为 false, 然后 “bTreeNode = 栈顶->右孩子” 开始遍历他的右子树. 当p的右子树都遍历完了之后(也就是p的右子树都依次出栈了之后)又会遍历到p自己, 不过这一次他的 isFirstTime_ 标志已经为 false 了, 我们通过这个标志知道不是第一次遍历到p了, 所以这时我们使p出栈( 此时p的右子树都已经遍历完了, 所以不用像之前一样再 “bTreeNode = 栈顶->右孩子” 了 )
1 | void PostOrderTraverseNonRecursion( btnp bTreeNode ) |
遍历测试代码
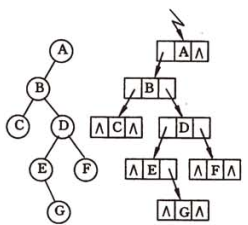
如上图得到的相应的三种深度优先遍历的序列分别为 :
- 先(根)序遍历 : ABCDEGF
- 中(根)序遍历 : CBEGDFA
- 后(根)序遍历 : CGEFDBA
而得到的广度优先遍历的序列为 : ABCDEFG
遍历测试代码CPP版
参照上图构建如下二叉树 :
1 |
|
遍历测试代码GO版
1 | package main |
深度优先的迭代式遍历之总结
请仔细看完上述代码再看总结, 才更有体会.
- 出栈条件的不同:
- 前序遍历的出栈条件都是左边走到头了就让栈顶元素出栈
- 中序遍历同上
- 后序遍历的出栈条件是遍历到同一个栈顶元素第二次要出栈的时候才让他出栈
- 打印结点时机的不同:
- 前序遍历的打印结点时机是入栈时就打印
- 中序遍历的打印结点时机是第一次出栈时就打印
- 中序遍历的打印结点时机是第二次出栈时就打印
交换所有左右孩子
非递归方式Swap
1 | void SwapBT( btnp bTreeNode ) |
递归方式Swap
交换左右孩子用递归很容易做到
1 | void SwapBinaryTree(BTNP btnp) |